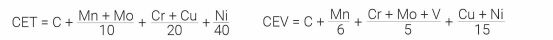General Product Description
AR235 steel plate is a carbon-manganese steel product with a nominal hardness of 235 Brinell (HBW). It is intended for moderate wear applications. AR235 is available as mill plate, temper leveled plate or as coils. AR235 is not intended for structural applications.
Applications
Typical applications for AR235 steel plate include cement mixer drums and fins, bulk material handling chute liners, skirtboard liners, and screw conveyers.
Available Dimensions
(in)
(in)
(in)
(in)
(in)
(in)
(in)
(in)
(in)
Mill Plate: Please inquire for plate thicknesses less than 0.500 inches down to 0.375" and over 0.750 inches up to 1.0 inches, widths less than 72 inches and greater than 120 inches, and for plate lengths less than 120 inches and greater than 1020 inches.
Temper Leveled Plate: SSAB's Cut-To-Length facilities use the temper leveled coil (TLC) process to produce temper leveled plate products. For additional information concerning our temper leveling process, please refer to our SSAB Americas: North American Cut-to-Length Operations brochure located under the Downloads section of our Commercial Steels Overview page.
Coils: Inquire for thicknesses greater than 0.375 inches and for widths less than and greater than 96 inches wide.
Mechanical Properties
AR235 has a nominal hardness of 235 HBW. It is produced to a specified chemical composition only; if an application requires specific mechanical properties it should be inquired. Brinell hardness, if specified, is tested according to ASTM A370, on a surface milled or ground from 0.020” to 0.118” (0.5 - 3.0 mm) below the plate surface. Typical hardness range is 200 to 280 HBW. Inquire for other HBW requirements.
Chemical Composition
Maximum wt % based on ladle analysis.
(max %)
(max %)
(max %)
(max %)
(max %)
(max %)
(max %)
Carbon Equivalent
Tolerances
Tolerances for Mill Plate:
Thickness, width and length tolerances for AR235 are in accordance with ASTM A6. ASTM A6 Standard flatness tolerance is available for thicknesses less than 0.500 inches and ASTM A6 Half-Standard Flatness tolerances are available for plate thicknesses of 0.500 inches to 1.0 inch. Inquire for specific mill flatness capabilities.
Tolerances for Temper Leveled Plate:
Thickness, width and length tolerances for AR235 are in accordance with ASTM A6. ASTM A6 Half-Standard Flatness tolerances or better are available for temper leveled plates. Flatness capabilities are determined by the processing line and the minimum yield strength of the material.
Tolerances for Coils for Conversion To:
For minimum gauge orders, thickness and width tolerances are in accordance with the respective ASTM specifications of A568 for thicknesses of less than 0.230 inches(exclusive), and A635 for thicknesses of 0.230 inches to 1.00 inch, inclusive. Thickness tolerances are in accordance with Table S1.1 found in each of the ASTM specifications of A635 and A568, respective of thickness. Width tolerances are in accordance with Table 6 of ASTM A568 and Table 3 of ASTM A635. Thickness tolerances for nominal gauge orders must be inquired.
Cutting
AR235 steel plate can be thermally cut satisfactorily. The hardened, heat-affected zones adjacent to the cut surfaces should be removed before any subsequent forming or welding operation.
Formability properties
AR235 may be employed in moderate cold forming applications. Proper edge preparation (i.e. removal of hardened heat-affected zones adjacent to the cut surfaces) is essential to minimize the potential for cracking. Cold forming should be performed at a minimum temperature of 68°F (20°C). Minimum recommended punch radius, R, and die width opening, W, as a function of bending orientation is provided in the following table.
Weldability
AR235 is weldable by conventional electric arc welding processes when using low-hydrogen consumables and appropriate welding practices. The following recommendations should be considered.
When matching consumables are not required, lower strength electrodes are recommended. Slow-cooling after welding and a post-weld heat treatment at 1100°F (595°C) are suggested to minimize cold cracking. The electrodes for shielded metal arc welding must be properly stored and dried; the welding flux must be properly dried and free from moisture for submerged arc welding.